Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Structures And Ligaments Of The Shoulder Joint. | Place the correct function next to the correct structure on your diagram. Cartilage ligaments other tissues that connect bones tendons bones. How would you label the x and y axes? Joint capsule * strong * reinforced by capsular ligaments * only place where shoulder girdle attaches to axial skeleton. Ligaments reinforce joints by holding the bones together.
The activity of dtxr is regulated by iron which act. Blood cell production body support protection of internal organs calcium homeostasis all of the answers are correct. Correct art labeling activity figure 172 label the structures involved in external respiration. Dna polymerase begins synthesizing the lagging strand by adding nucleotides to a short segment of rna. No ligaments connect the bones at this joint.
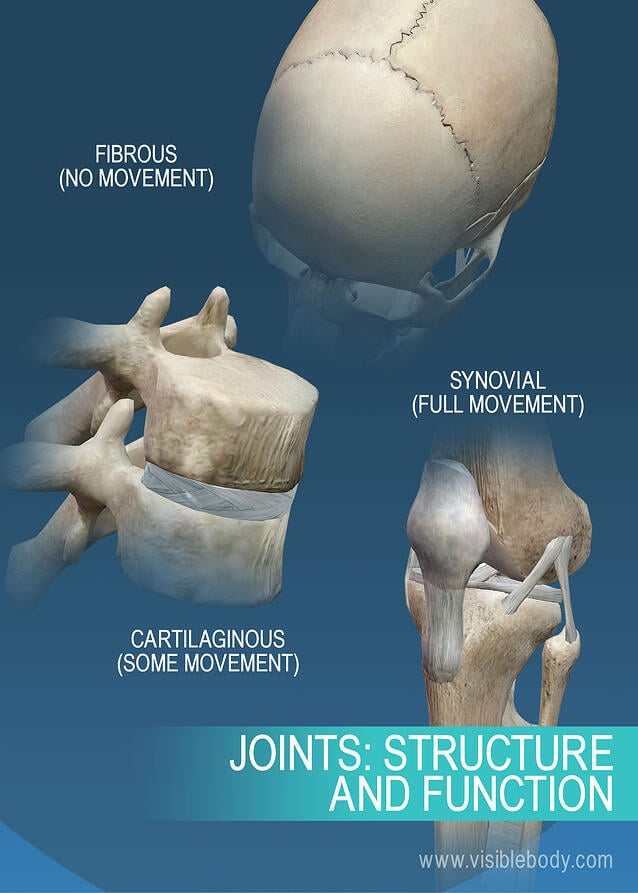
Joints of shoulder region at cram.com. A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. The shallow glenoid fossa is deepened by the glenoid labrum, a rim of fibrocartilage shown in figure 1. Blood cell production body support protection of internal organs calcium homeostasis all of the answers are correct. Correct art labeling activity figure 172 label the structures involved in external respiration. They lack mitochondria, but other eviden … ce shows them to be most closely related to members of the excavates. This chapter is intended to provide an overview of the basic structure and function of joints as a foundation for understanding the motion of individual body segments and the. Drag the correct labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and molecules involved in translation. The next true anatomical joint is the acromioclavicular joint. Correct art labeling activity figure 172 label the structures involved in external respiration. • identify the components of a synovial joint. This diagram here just shows the joint capsule itself. • lie on your back on a firm surface.
The transverse humeral ligament is not shown on this diagram. No ligaments connect the bones at this joint. Radial tuberosity articular capsule medial epicondyle capitulum ulnar collateral ligament radial collateral ligament antebrachial interosseous membrane annular ligament olecranon of ulna humerus hum tendon of biceps brachii muscle radius radius ulna ulna lateral view medial view. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the types of synovial joints. Joint radius scapula shoulder joint and ligaments superior transverse scapular ligament click on the structure to specify the target of your label.

Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. How the shoulder joint works. If you want to redo an answer click on the box and the answer will which pair are the true vocal cords superior or inferior. • explain how tendons and ligaments support the structure of a joint. Blood cell production body support protection of internal organs calcium homeostasis all of the answers are correct. Translation of oppenheim s 1911 paper on dystonia klein 2013. Looking at the tree for eukaryotes, what can you conclude about the monocercomonoides. Drag the labels onto the. • lie on your back on a firm surface. Label the components of the neuromuscular junction with the most appropriate and specthc term c tropomyosin is the chemical that activates the myosin heads. Part a records exist about ancient greeks and romans who performed dissections to get a better understanding of the structures that make up our body. The next true anatomical joint is the acromioclavicular joint. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement.
They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. * fibrous structure around the glenoid fossa. Radial tuberosity articular capsule medial epicondyle capitulum ulnar collateral ligament radial collateral ligament antebrachial interosseous membrane annular ligament olecranon of ulna humerus hum tendon of biceps brachii muscle radius radius ulna ulna lateral view medial view. When an antigen is bound to a class ii mhc protein it can activate a cell. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the bone markings.
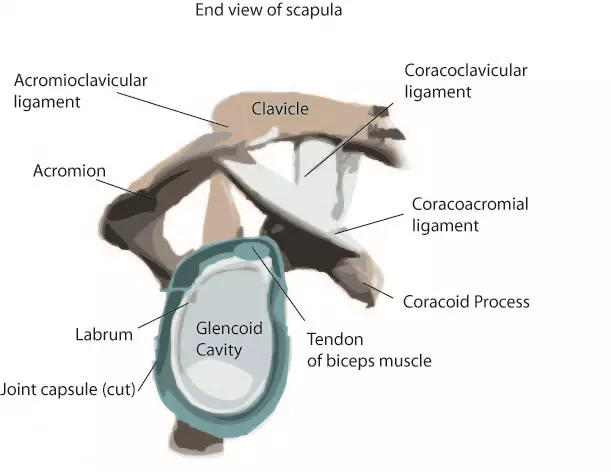
Shoulder pain the synovial membrane, capsule, and ligaments of the shoulderjoint are innervated by the axillary nerve and the suprascapular nerve. Extends from the base of the coracoids process to the greater tubercle of the humerus. Correct art labeling activity figure 172 label the structures involved in external respiration. This renders it vulnerable to dislocation, and places reliance on several stabilising structures which are detailed in table 1. Ligaments reinforce joints by holding the bones together. Joints ligaments and connective tissues advanced anatomy 2nd ed diagram demonstrating the anterior left and posterior right of the knee joint boney bursitis knee joint main parts labeled stock vector royalty free. The next true anatomical joint is the acromioclavicular joint. It is important to appreciate that pain in the shoulder region can be caused by disease elsewhere and that the shoulder joint may be normal; • lie on your back on a firm surface. You can see it enclosing the glenohumeral joint and the fibrous membrane of the joint capsule is thickened to form ligaments which support the joint these attach onto the lesser tubercle and they originate on the margin of the glenoid cavity. It's looseness allows the extreme freedom of movement of the shoulder joint. How the shoulder joint works. When an antigen is bound to a class ii mhc protein it can activate a cell.
Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Structures And Ligaments Of The Shoulder Joint.: • lie on your back on a firm surface.
comment 0 Post a Comment
more_vert